- srushtigastro@gmail.com
- +91- 8073380392
24 hours PH manometry
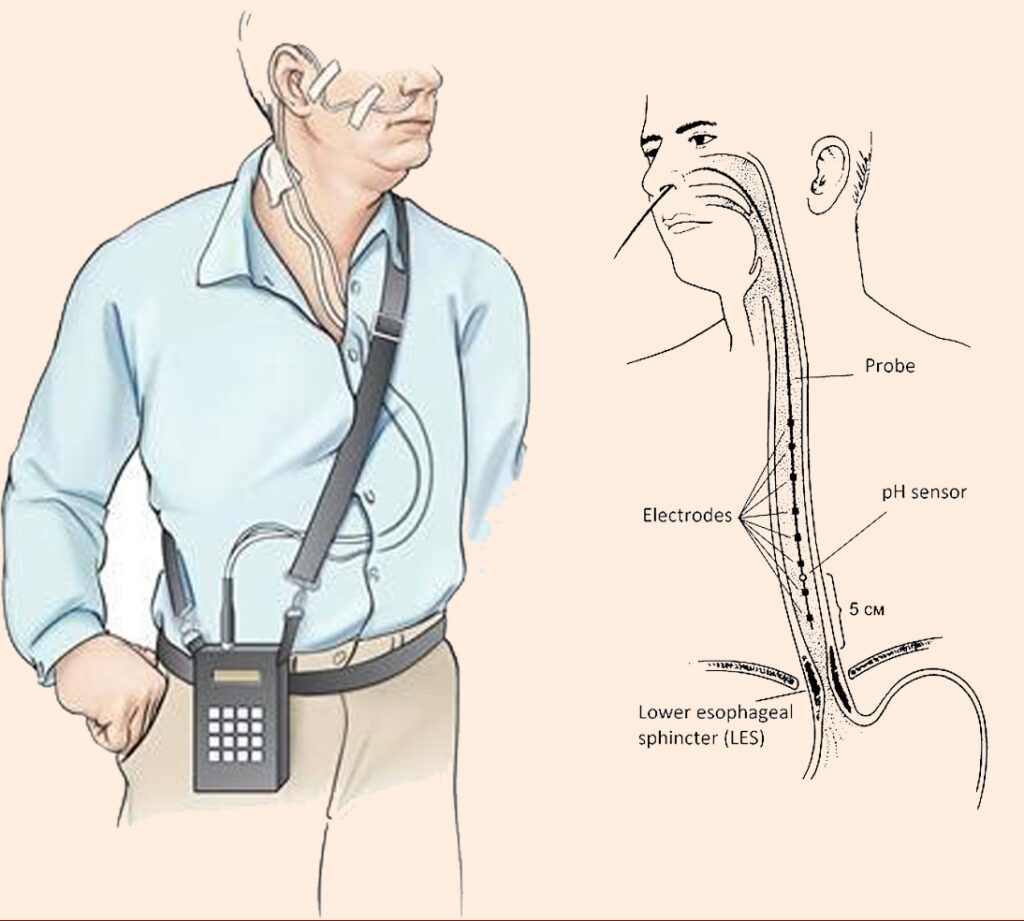
24-Hour pH manometry is a comprehensive diagnostic tool that provides valuable insights into the acidity levels within the esophagus over an extended period. During the procedure, a thin tube equipped with a pH sensor is inserted through the nose or mouth and positioned in the lower esophagus. This sensor continuously monitors the pH levels of the esophageal environment, recording any episodes of acid reflux or abnormal acidity throughout the day and night. Patients are typically instructed to maintain their usual activities and diet during the monitoring period to capture a representative profile of their acid exposure.
This diagnostic test offers clinicians a detailed understanding of the frequency, duration, and severity of acid reflux episodes, helping to confirm or rule out GERD and guide treatment decisions. It can distinguish between acidic and non-acidic reflux, providing valuable information for tailoring treatment approaches. By correlating pH measurements with symptoms reported by the patient, healthcare providers can assess the impact of acid reflux on an individual’s quality of life and devise personalized management strategies.
Benefits:
In summary, 24-hour pH manometry is a valuable diagnostic tool that plays a crucial role in the assessment and management of GERD and other esophageal disorders, offering clinicians invaluable insights into acid reflux patterns and guiding personalized treatment strategies.
Empowering assistance, right when it matters. We’re here to lend a hand whenever you need it.

Call : +91- 8073380392
srushtigastro@gmail.com
Srushti Gastro & liver Clinic 186, 165, 9th Main Rd, Sector 6, HSR Layout, Bengaluru, Karnataka 560102