- srushtigastro@gmail.com
- +91- 8073380392
GI Cancers
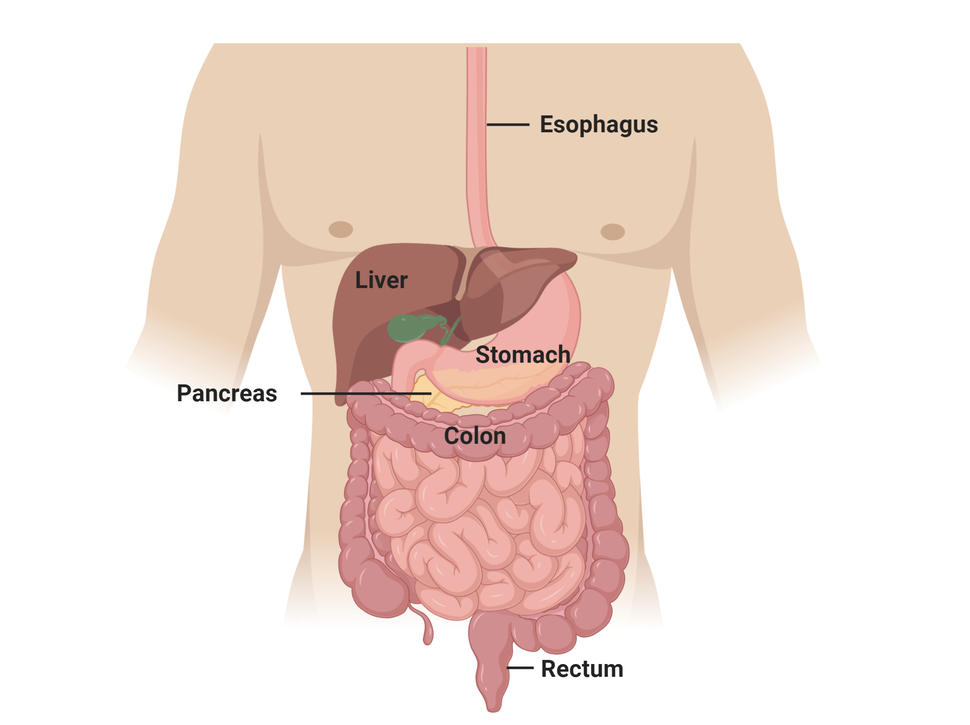
Gastrointestinal (GI) cancers encompass a group of malignancies that originate in various parts of the digestive tract, including the esophagus, stomach, liver, pancreas, gallbladder, small intestine, colon, and rectum. These cancers can develop from different types of cells within the gastrointestinal system and may present with varying symptoms and prognoses.
The symptoms of GI cancers can vary depending on the specific type and location of the malignancy. Common signs may include abdominal pain or discomfort, changes in bowel habits, unexplained weight loss, difficulty swallowing, persistent indigestion or heartburn, jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes), blood in the stool or vomit, and fatigue.
Early detection and diagnosis are crucial for effectively managing GI cancers and improving patient outcomes. Screening tests such as colonoscopy, endoscopy, imaging studies (e.g., CT scans, MRIs), and blood tests may aid in the early detection of GI malignancies. Treatment options for GI cancers may include surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, targeted therapy, immunotherapy, or a combination of these modalities, depending on the type and stage of the cancer.
Looking for the best GI Cancers Treatment in HSR Layout? Contact us today.
Benefits:
Overall, understanding GI cancers, promoting early detection and treatment, and implementing preventive measures can significantly impact patient outcomes, reduce the burden of disease, and improve the overall well-being of affected individuals and communities.
Empowering assistance, right when it matters. We’re here to lend a hand whenever you need it.

Call : +91- 8073380392
srushtigastro@gmail.com
Srushti Gastro & liver Clinic 186, 165, 9th Main Rd, Sector 6, HSR Layout, Bengaluru, Karnataka 560102